Sky watch tonight: Orion rising in the southeast
-
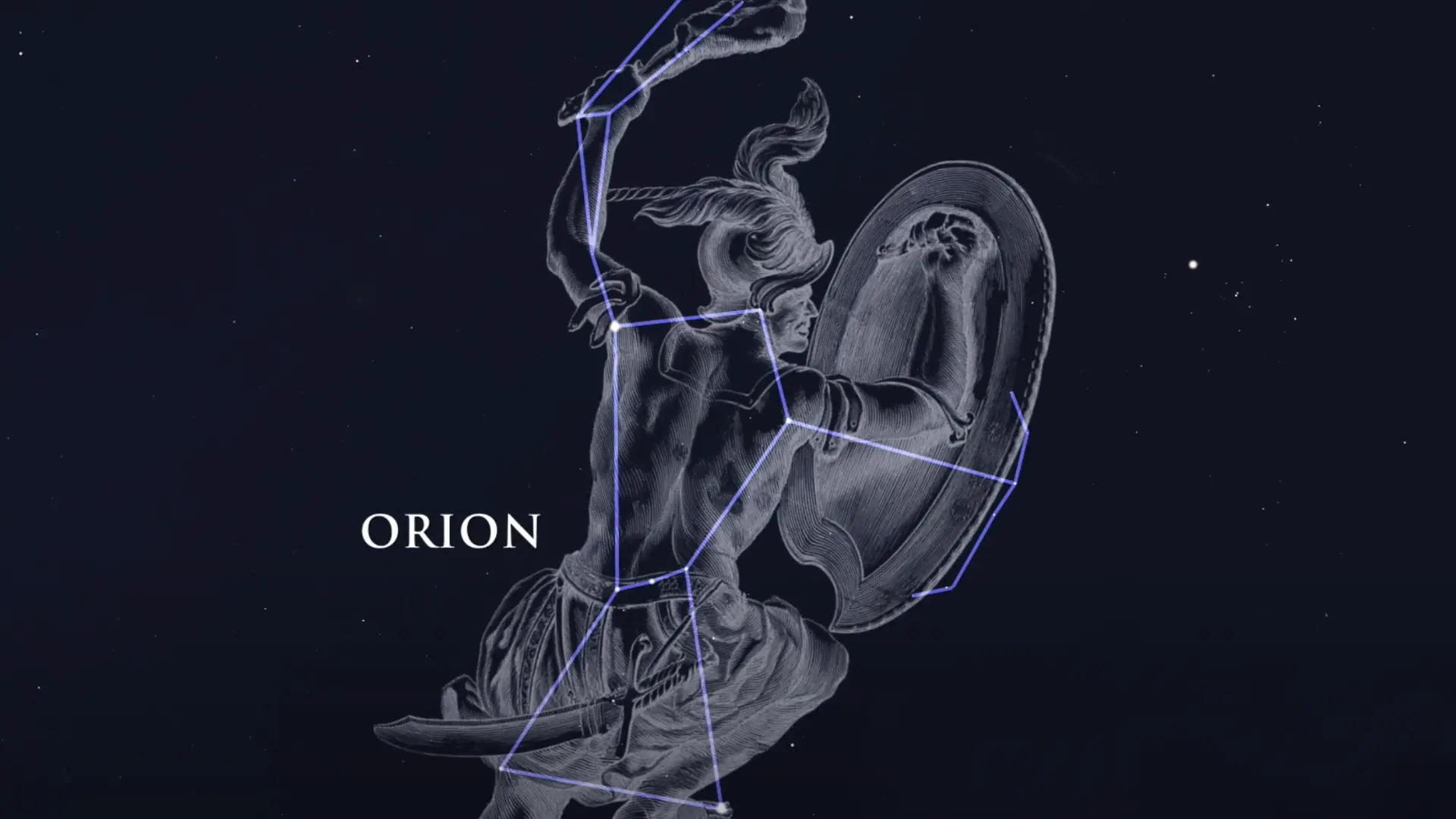 Orion constellation (Image via NASA)
Orion constellation (Image via NASA)Tonight, that is on Monday, December 8, 2025, skywatchers will be able to see the constellation Orion in the Northern Hemisphere’s southeastern sky by 9 p.m. at night.
The whole of Orion’s Belt, which contains a star pattern of three blue supergiant stars, namely Alnitak on the left side of the Belt, Alnilam in the middle, and Mintaka in the right, forming a linear structure, will be visible, alongside Orion’s sword, also clear to see.
However, the Orion, the middle star in the Sword remains unclear to the unaided eye since it is the Orion Nebula, “the brightest stellar nursery to Earth.” Composed of gas and dust, it is a robust site for the emergence of young stars, including the Trapezium cluster.
Details about the constellation Orion's origin, and more about its features
The constellation Orion is famously named by the Greeks after the mythological hunter Orion, because they saw the shape of the constellation to resemble a “giant hunter with a sword.”
NASA describes the constellation as "one of the most recognizable" constellations that can be spotted by those interested easily.
According to NASA, the “easiest way” to spot the constellation is to look for “three bright stars close together in an almost-straight line” in a clear night sky.
The triad of stars is called the Orion’s belt, with the two north-facing stars resembling the hunter’s shoulders and the one in the south representing his feet.
Although the stars in the Orion’s Belt appear close by when observed from Earth, they are actually widely spaced.
“For example, Alnitak, the star at the left side of Orion's belt, is about 800 light-years away," NASA says.
As for Alnilam, it is approximately 1,300 light-years away, whereas Mintaka is about 900 light-years away, as per NASA's records.
As for the “superstars” of Orion, there are two that stand out from the lot – Betelgeuse and Rigel.
Betelgeuse is a “red supergiant” on the right side of Orion, whereas Rigel is the “blue supergiant” on the left foot of Orion.
However, there is always more that meets the eye. While the “stars” that make up Orion’s Belt appear as individual entities, they are actually a collection.
But it is difficult to notice when observed from a distance. For example, Mintaka, the star on the right of the Belt, is a “complex star system” of five stars.
Other major events in December 2025 that sky watchers can look forward to
On December 7, skywatchers witnessed the moon and Jupiter conjunction, following which, they can observe the Orion constellation on December 8.
The week after that, on December 13 and 14, the Geminid Meteor Shower will become visible to the skygazers.
On December 19, the much talked-about event will occur. The interstellar object, 3I/ATLAS, will come the closest to Earth, helping scientists and enthusiasts across the globe gather more information about it.
According to NASA, skygazers can spot the object "looking east to northeast in the early pre-dawn morning." At that time, 3I/ATLAS will come "right under Regulus" - a star at the centre of constellation Leo.
Since its discovery in July, 3I/ATLAS has caused quite the buzz in the astronomy community.
December 19 will mark an important day for researchers, as they will get to study the mysterious object at its closest distance to Earth.
Stay tuned for more updates.
TOPICS: Orion, Constellation, Night sky December, Night sky watch